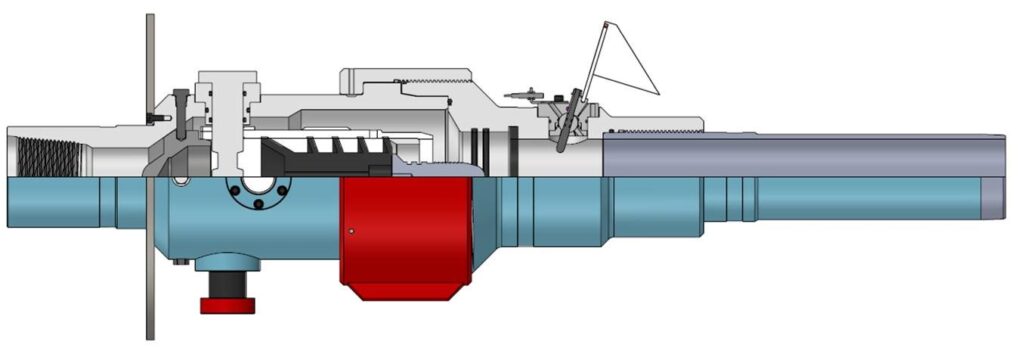
Cement Head Pump Around Plug
Good cement bonds are required when cementing well bore casings into wells. Poor cement bonds can result in formation pressures and fluids breaching to the surface or into other formations downhole. This will result in surface or underground blowouts and a loss of well control.
Cement bonds are usually better in vertical wells than those found in directional or horizontal wells. It is usually more difficult to centralize casing in horizontal wells than vertical wells. Cement slurries will usually find the easiest circulation path from the bottom of the well to surface. On directional wells, this path is usually the upper portion of the horizontal well while the casing lies on the lower portion of the well. Movement of the casing during cement circulation is usually the best way to disrupt any type of cement channeling and reduce torsional loads to the casing and connections. Rotating and reciprocating the casing can create alternating laminar and turbulent flows of the cement, reducing channeling, and trapped drilling fluids.
Currently, some cement heads require piping tied to the top of the head, impeding any rotation. Some cement heads without piping may only allow rotation or reciprocation independently. Other types will allow rotation and reciprocation simultaneously, but require casing movements or fluid pumping to stop, to load plugs or to divert flow.
Like the Core Design Cement Head that uses a hollow top plug (CMT-PTP), the Cement Head Pump Around Plug (CMT-PAP) will also allow rotation, reciprocation, pumping and plug launching simultaneously. The top of the CMT-PAP is connected directly to the top drive, while the bottom of the CMT-PAP is connected directly to the casing. This allows rotation and reciprocation of the casing simultaneously. The top plug (located inside the CMT-PAP) is a standard solid top plug, and all circulation passes directly around the plug. Deployment of the solid top plug from the CMT-PAP is achieved by mechanically shifting a shaft that retains a plug retainer pot. Further downward movement of the pot will seal, allowing the pumping pressure to force the top plug out of the pot, past the retainer ring, and down the casing. The top plug ball can be launched on the fly (without stopping pumps) if required. The plug can also be launched without stopping casing movements.
APPLICATION:
- Cementing casing in vertical, directional, and horizontal drilled well bores.
FEATURES:
- Rotation and reciprocation of the casing at the same time during casing cementing.
- Top plug can be launched without stopping pumping procedures or casing movements.
- No hazardous cementing lines are tied into cement head.
- No stopping cement process to tighten leaks as cement headlines are eliminated.
- No premature launching of top plugs (vacuum) during valve changing, pump stoppage mechanical monitoring system to show launching (movement) of the top plug.
- Designed to work with conventional and slant style drilling rigs.
- Mechanical launching of plugs.
- Latch down plugs and rings available.
BENEFITS:
- Increase better cement bonds in any type of well to be cemented.
- Quicker and safer operations of the cement head, minimizing the risk of getting casing stuck during the cementing process.
- Decrease chances of air voids in cement and wet shoes.
- Decrease volume of cement slurry required (cost savings).